UPSC Key: Operation Sindoor 2025, Ricardian theory and Global Space Exploration Conference (GLEX)
Why strategic significance of Operation Sindoor 2025 is relevant to the UPSC exam? What is the significance of topics such as India’s past military operations against Pakistan, India-UK FTA and U.S. Federal Reserve on both the preliminary and main exams? You can learn more by reading the Indian Express UPSC Key for May 8, 2025.
 UPSC Key May 2025: Here's what you should be reading from the May 8, 2025 edition of The Indian Express
UPSC Key May 2025: Here's what you should be reading from the May 8, 2025 edition of The Indian Express
Important topics and their relevance in UPSC CSE exam for May 8, 2025. If you missed the May 7, 2025 UPSC CSE exam key from the Indian Express, read it here
FRONT PAGE
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
Mains Examination:
• General Studies II: India and its neighbourhood- relations
• General Studies III: Role of external state and non-state actors in creating challenges to internal security
What’s the ongoing story: India today hit nine sites in Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Kashmir, targeting terrorist infrastructure there. The strike came two weeks after the Pahalgam terror attack, in which 26 people were killed.
Key Points to Ponder:
• Operation Sindoor 2025—What you know about the same?
• Why Operation Sindoor?
• What signals did the Indian military action send?
• Do you think that India’s response on 7th May 2025 was just about the terrorist attack in Pahalgam last month?
• What is the strategic significance of Operation Sindoor 2025 in the context of India’s counter-terrorism policy and regional security dynamics?
• What is a precision weapon?
• How India used precision weapons under Operation Sindoor?
• Know the role of precision airstrikes in modern warfare, with reference to India’s use of Rafale jets and SCALP missiles during
Operation Sindoor 2025.
• What are the scalp missile?
• What is a HAMMER Missile?
Key Takeaways:
• A defence ministry statement said on Wednesday, “A little while ago, the Indian armed forces launched ‘Operation Sindoor’, hitting terrorist infrastructure in Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Jammu and Kashmir from where terrorist attacks against India have been planned and directed.”
• “Our actions have been focused, measured and non-escalatory in nature. No Pakistani military facilities have been targeted. India has demonstrated considerable restraint in selection of targets and method of execution,” it said.
• “These steps come in the wake of the barbaric Pahalgam terrorist attack in which 25 Indians and one Nepali citizen were murdered. We are living up to the commitment that those responsible for this attack will be held accountable,” it said.
• In a post on X, the Additional Directorate General of Public Information, Indian Army, posted an image that read Operation Sindoor with the text: #PahalgamTerrorAttack. Justice is Served. Jai Hind!
• The Reuters news agency, reporting from Muzaffarabad in PoK, said multiple explosions had been heard. It quoted a spokesman for Pakistan’s military telling broadcaster ARY that India had attacked Pakistan with missiles in three places and that Pakistan would respond.
• New York Times reported that residents of Muzaffarabad also reported hearing jets flying above. They said that a site in a rural area near Muzaffarabad that was once used by Lashkar-e-Taiba appeared to have been targeted in the strikes.
• A spokesman for the Pakistan Army said that two other places had also come under attack. One was Bahawalpur, in Pakistan Punjab Province, the site of a religious seminary associated with Jaish-e-Mohammad, and the other was Kotli, a city in Pakistan-occupied Kashmir.
Do You Know:
• Earlier in the day, weighing its response to the Pahalgam terror attack, the government was learnt to be working on a multi-pronged military strategy to re-establish deterrence against Pakistan’s hostile behaviour.
• This was the main and clear brief given to the military and security establishment by the political top brass over the last week of consultations. The process, sources had told The Indian Express, would look at all credible options, including a military retaliation, but the objective of “re-establishing deterrence” was firmly set.
• There was a growing realisation within the top levels of the government that the deterrence established by the Balakot air strike in February 2019 had “worn off”, and it was time to re-establish that, sources had said.
• Wednesday’s development follows a series of high-level meetings of Prime Minister Narendra Modi with National Security Advisor Ajit Doval, Navy chief Admiral Dinesh K Tripathi, IAF chief Air Chief Marshal A P Singh to discuss operational preparedness and retaliatory options on the table.
• At the tactical level, the Army has bolstered forward defences along the borders, while additional strengthening and preparations are underway to tackle any cross-border action.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍WITH NINE STRIKES, INDIA UNDERLINES NEW MESSAGE TO PAK
📍Operation Sindoor signals: Three takeaways from India’s action against Pak terror
Previous year UPSC Mains Question Covering similar theme:
📍The terms ‘Hot Pursuit’ and ‘Surgical Strikes’ are often used in connection with armed action against terrorist attacks. Discuss the strategic impact of such actions. (2016)
EXPRESS NETWORK
Cactus Lily to Bandar: India’s ops against Pak
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
Mains Examination: General Studies II: India and its neighbourhood- relations.
What’s the ongoing story: Almost all past military operations by India against Pakistan have largely had conventional military names.
Key Points to Ponder:
• India’s past military operations against Pakistan—know in detail
• Why did the Indian Army name operation Sindoor?
• How by naming Operation Sindoor, the Indian defence establishment has made a marked shift?
• How do military operations get their names?
• Know the evolution of India’s military response mechanisms to cross-border terrorism since the Kargil War.
• How has technological advancement played a key role in Operation Sindoor 2025?
Key Takeaways:
• By naming the operation to hit terrorist infrastructure at nine sites in Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Kashmir as Operation Sindoor, the Indian defence establishment has made a marked shift – from the projection of military power to paying tribute to the victims of the Pahalgam terror attack.
• Government sources indicate the name of the operation was chosen by Prime Minister Narendra Modi himself and could be seen as a tribute to the women who lost their husbands in the April 22 attack at the Baisaran meadow that killed 25 tourists and a local.
• Almost all past military operations by India against Pakistan have largely had conventional military names to inspire confidence internally and send a message of strength externally. Sometimes names were chosen to maintain the secrecy of the operation, and, at times, names were even drawn from Indian mythology.
• In the past, India has used names such as Operation Riddle, Operation Ablaze, Operation Cactus-Lily, Operation Trident, Operation Python, Operation Meghdoot, Operation Vijay, Operation Safed Sagar, and Operation Bandar in conflicts with Pakistan.
Do You Know:
Here’s a look at some of the past military operations by India against Pakistan:
• Operation Riddle (1965 Indo-Pak War): Operation Riddle was the Indian military’s response to the offensive launched by Pakistan under the code names of Operation Gibraltar and Grand Slam in 1965. As Pakistan violated the Line of Control (LoC) and entered Jammu and Kashmir, India launched this operation, targeting Lahore and Kasur on September 6, 1965. The operation had a crippling effect on the Pakistan military.
• Operation Ablaze (1965 Indo-Pak War): Operation Ablaze, too, was in the context of the 1965 Indo-Pak war. Launched as a defensive strategy on the western border, Operation Ablaze was the Indian Army’s pre-emptive mobilisation plan in April 1965, following rising tensions and skirmishes along the India-Pakistan border, particularly in the Rann of Kutch area.
—Although it did not immediately result in direct combat, this large-scale mobilisation demonstrated India’s readiness. The operation set the stage for heightened military preparedness before the full-fledged war broke out in August 1965.
• Operation Cactus Lily (1971 Indo-Pak War): Operation Cactus Lily, also known as The Meghna Heli Bridge or the Crossing of the Meghna, was an air assault operation conducted in December 1971 during the Bangladesh Liberation War. It was conducted by the Indian Army and Indian Air Force to cross the Meghna River, bypass a Pakistani stronghold at Ashuganj/Bhairab Bazar and reach Dhaka.
• Operations Trident and Python (1971 Indo-Pak War): Both were offensive operations launched by the Indian Navy on Pakistan’s port city of Karachi during the Indo-Pak War of 1971. Operation Trident saw the first use of anti-ship missiles in combat in the region. The operation was conducted on the night of December 4-5, 1971 and inflicted heavy damage on Pakistani vessels and facilities.
• Operation Meghdoot (Siachen conflict): By 1984, Pakistan’s cartographic aggression in the uncharted territory of Ladakh, allowing foreign mountaineering expeditions in Siachen, was becoming a cause of concern. Having received intelligence inputs about an impending Pakistani military action in the area, India decided to thwart Pakistan’s efforts to legitimise its claim on Siachen.
—The Indian Army launched Operation Meghdoot in April 1984 to secure strategic heights on Siachen with the deployment of troops. The IAF transported stores and troops and air-dropped supplies to high-altitude airfields, from where Mi-17, Mi-8, Chetak, and Cheetah helicopters ferried men and material to dizzying heights on the glacier.
• Operation Vijay (1999 Kargil conflict)—Operation Vijay was the codename for the Indian military operation launched in May 1999 to reclaim areas occupied by Pakistani forces during the Kargil War. The operation successfully forced Pakistani troops to withdraw and recapture critical positions, leading to India’s victory.
• Operation Safed Sagar (1999 Kargil conflict: Operation Safed Sagar was the codename for the Indian Air Force’s role in the 1999 Kargil War. It involved a series of airstrikes to flush out Pakistani troops from Indian positions in the Kargil sector along the Line of Control. This was the first large-scale use of air power in the region since the 1971 Indo-Pakistani War.
• Unnamed operation (2016 surgical strikes): This operation, conducted by Indian special forces in response to the Uri attack, was not given any specific name other than surgical strikes. It targeted terrorist launch pads across the LoC in Pakistan-administered Kashmir.
• Operation Bandar (2019 Balakot air strikes): This was in response to the February 2019 attack by operatives of the Jaish-e-Mohammed on a CRPF convoy in Jammu and Kashmir that killed 40 soldiers. Under Operation Bandar, the Indian Air Force carried out air strikes on a Jaish-e-Mohammed training camp in Balakot, Pakistan, where it claimed to have killed several terrorists.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍Haseeb Drabu writes: How missile strike in Pakistan and PoK is India’s diplomatic gain on Kashmir
Previous year UPSC Prelims Question Covering similar theme:
1. Operations undertaken by the Army towards upliftment of the local population in remote areas to include addressing of their basic needs is called: (2024)
(a) Operation Sankalp
(b) Operation Maitri
(c) Operation Sadbhavana
(d) Operation Madad
THE IDEAS PAGE
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance
Mains Examination: General Studies II: Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
What’s the ongoing story: Rajat Kathuria Writes:With multilateralism in an indefinite coma, for India, well-negotiated FTAs can play a role similar to that played by global markets and the WTO in the upscaling of the Chinese economy.
Key Points to Ponder:
• India and the UK signed a Free Trade Agreement (FTA)—know the key highlights
• Why the UK formally exited the EU and how it impacted UK’s trade and market?
• What is Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership or CPTPP?
• For UK, the FTA with India is its most significant trade deal since leaving the EU—Why?
• ‘For a trade economist, the FTA is a manifestation of the Ricardian school of thought based on comparative advantage’—discuss
• What is Ricardian theory?
• The India-UK FTA is beneficial to both countries—how?
Key Takeaways:
Rajat Kathuria Writes:
• India and the UK signed a Free Trade Agreement (FTA) on May 6, marking the culmination of over three years of negotiations that began in January 2022. By the standards of negotiating timelines, the FTA has been rather swift.
• The one with the EU, in particular, has been languishing for almost two decades, although it seems to have picked up momentum of late. The other vital trade pact on the government’s anvil, with the US, was not in serious contention until earlier this year.
• Timing, after all, is everything. The UK formally exited the EU in December 2020 and has been seeking new trade relationships to compensate for the loss of EU market access. Since then, it has struck deals with Japan, Singapore, Vietnam and even entered the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership or CPTPP — a mega trade bloc of 12 countries.
• In many ways, the FTA with India is its most significant trade deal since leaving the EU because India is one of the world’s fastest-growing major economies.
• India offers a young and digitally savvy consumer base with opportunities for British technology, education, and professional services. The attention towards diversification away from China, coupled with India’s strong economic trajectory, presents the UK with a rare opportunity.
• India recognises the inevitability of engaging more with the outside world to achieve its ambition of a “viksit” India by 2047. This goal could remain unrealised without enhanced global engagement and trade.
Do You Know:
• The total bilateral trade between India and the UK touched approximately £42 billion by mid-2024 with India maintaining a trade surplus of about £8 billion. The FTA aims to double trade by 2030. The UK ranks as the sixth-largest investor in India, with cumulative investments exceeding £38 billion over the past three years in sectors like financial services and manufacturing was the second largest source of FDI in the UK in 2023.
• The Ricardian school of thought, a foundational school within classical economics, is primarily known for its emphasis on comparative advantage and the labour theory of value. This school, heavily influenced by the works of David Ricardo, argues that free trade benefits all participating nations, even those with an absolute advantage in production, because they can specialize in what they do most efficiently and trade with others.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍UK-India Free Trade Agreement (FTA) signed: the key goods included, what it means
Previous year UPSC Prelims Question Covering similar theme:
2. The term ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership’ often appears in the news in the context of the affairs of a group of countries known as(2016)
(a) G20
(b) ASEAN
(c) SCO
(d) SAARC
EXPRESS NETWORK
Direct and clear objectives to collaborate with ISRO: ESA chief
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
Mains Examination: General Studies III: Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, robotics, nano-technology, biotechnology and issues relating to intellectual property rights.
What’s the ongoing story: The European Space Agency (ESA) now has direct and clearer objectives to work with India and is open to collaborating on bigger and unexplored areas of space, said Dr Josef Aschbacher, the ESA director general.
Key Points to Ponder:
• What Joint Statement of Intent on Human Space Exploration says?
• What is Global Space Exploration Conference (GLEX) – 2025?
• Global Space Exploration Conference (GLEX), 2025—Know its key highlights
• What is the Bharatiya Antariksha Station?
• Area of cooperation included in the recent ISRO-ESA collaboration agreement—know in detail
• How the ISRO-ESA partnership can contribute to advancements in human spaceflight?
Key Takeaways:
• On Wednesday, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and ESA inked a Joint Statement of Intent on Human Space Exploration on the sidelines of the Global Space Exploration Conference (GLEX) – 2025.
• “ESA and ISRO have been collaborating for over 40 years. But we will jointly explore newer areas of space exploration together like never before,” the ISRO chairman, Dr. V Narayanan, said.
• Speaking to The Indian Express, Aschbacher said, “ESA is happy partnering with ISRO and we look forward to exploring large-scale space operations. It is a strong recognition both for ESA and ISRO to work together on a domain of space exploration. This is a complete new chapter in our relations.”
• While ISRO and ESA are yet to discuss the exact areas of collaboration, Wednesday’s agreement will now pave the way for greater discussions between the two space agencies and the process for which will get underway in the coming months.
• Two months ago, the ESA delegation visited India and held preliminary discussions. Collaborations are being keenly considered on India-proposed building of the Bharatiya Antariksha Station (BAS). India plans to build the space station by 2035. In a five-module design, the BAS-1 is scheduled for a launch in 2028.
• ESA is considering the utilisation of BAS once it is built and ready. It is also considering providing ISRO with cargo-delivery support in building the BAS.
• The components of the Indian space station are planned to be sent into space as different segments and docked once in space. Earlier this year, ISRO successfully performed the docking and undocking of two satellites in its SpaDeX mission — a demonstration and a skill which will be essential for future space activities like building the BAS.
Do You Know:
• The Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS), or Indian Space Station, is a planned modular space station in low Earth orbit (LEO). It is an ambitious project by the Indian government and ISRO to conduct scientific research, advance human spaceflight capabilities, and foster international collaborations in space. The BAS is expected to be operational by 2035, with the first module, BAS-1, launched in 2028.
• According to PIB, GLEX 2025 is designed to encouraging the sharing of programmatic, technical and policy information, as well as collaborative solutions, challenges, lessons learnt, and paths forward among all nations with the desire to explore space. During the 4 years since GLEX 2021 the international space exploration community will have significantly moved forward with their respective exploration planning and programmes and it is therefore timely to take stock of the developments and undertake an outlook to the future of space exploration on a global scale.
• The GLEX 2025 programme is designed to bring together leaders and decision-makers within the science and human exploration community – engineers, scientists, entrepreneurs, educators, agency representatives and policy makers. It will provide a forum to discuss recent results, current challenges and innovative solutions and it will contain several opportunities to learn about how space exploration investments provide benefits as well as discuss how those benefits can be increased through thoughtful planning and cooperation.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍NASA members forced to skip meet in Delhi
Previous year UPSC Prelims Question Covering similar theme:
3. Consider the following statements: (2016)
The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO
1. is also called the Mars Orbiter Mission
2. made India the second country to have a spacecraft orbit the Mars after USA
3. made India the only country to be successful in making its spacecraft orbit the Mars in its very first attempt
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Previous year UPSC Mains Question Covering similar theme:
📍What is India’s plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme? (2019)
EXPLAINED
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
Mains Examination:
• General Studies II: India and its neighbourhood- relations.
• General Studies III: Role of external state and non-state actors in creating challenges to internal security
What’s the ongoing story: Two weeks after Pakistani terrorists gunned down 26 civilians near Pahalgam in Jammu & Kashmir, India responded on Wednesday (May 7) with airstrikes on nine locations in Pakistan and Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK). Codenamed Operation Sindoor, these strikes targeted the terrorist infrastructure across the border and the Line of Control (LoC).
Key Points to Ponder:
• Which terrorist organizations were targeted during Operation Sindoor?
• What you know about Jaish-e-Mohamed or the Lashkar-e-Taiba?
• Which advanced weaponry was reportedly used by India during Operation Sindoor?
• The Resistance Front (TRF), linked to the Pahalgam attack, is believed to be an offshoot of which terrorist organisation?
• Know the role of Lashkar-e-Taiba and Jaish-e-Mohammed in past terrorist activities against India.
• What are the challenges and consequences of conducting precision strikes on foreign soil, considering international law and diplomatic relations.
• Know the historical patterns of terrorist attacks by groups like LeT and JeM and how India’s military responses have evolved over time.
Key Takeaways:
• “Over the last three decades, Pakistan has systematically built terror infrastructure. It is a complex web of recruitment and indoctrination centres, training areas for initial and refresh of courses, and launch pads for handlers,” Wg Cdr Vyomika Singh said during a press briefing on Wednesday morning.
• The targets were chosen “based on credible intelligence inputs” and so as to “avoid damage to civilian infrastructure and loss of any civilian lives”, Singh said.
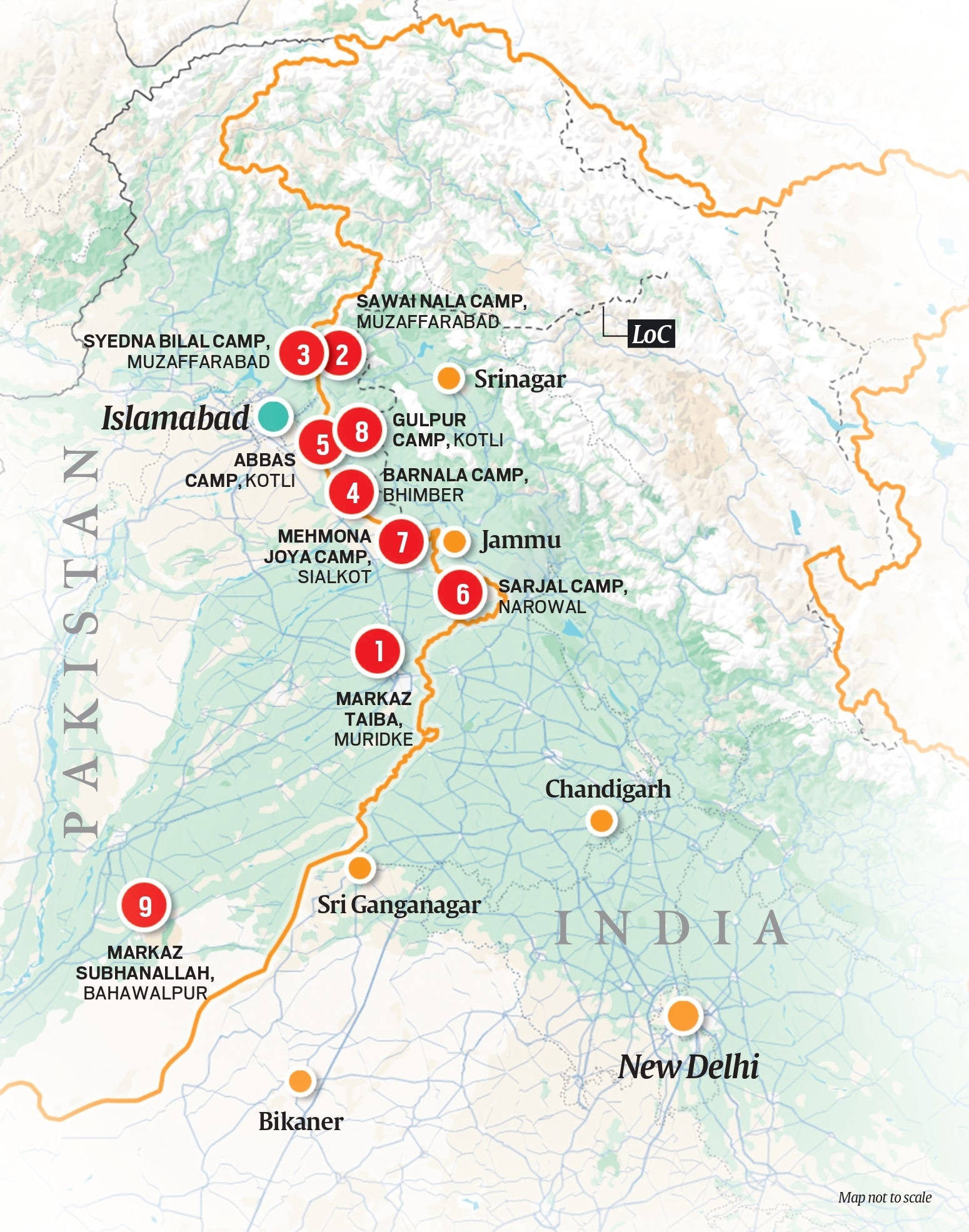 Operation Sindoor map; not to scale.
Operation Sindoor map; not to scale.
• These terrorist camps are linked with the Jaish-e-Mohamed or the Lashkar-e-Taiba.
• As The Indian Express has reported, Bahawalpur, which faces the Rajasthan frontier across the Thar desert, has been a stronghold of the Jaish-e-Mohammed, led by Maulana Masood Azhar. The Jamia Masjid Subhan Allah here is believed to be a hub of the JeM. Muridke near Lahore is the home of the Hafiz Saeed-led terror outfit Lashkar-e-Taiba. It houses the Markaz-e-Taiba, the base camp of the Lashkar-e-Taiba.
• Jaish-e-Mohammed or the Army of Mohammed (other names include Khuddam Ul Islam and Tehrik ul-Furqaan) was founded by Masood Azhar in the early 2000s. Azhar was designated a global terrorist by the UN in 2019.
• The Lashkar-e-Taiba and its co-founder Hafiz Saeed became household names in India after the 2008 Mumbai terror attacks, which killed more than 170 people. The Let also had a role in the 2006 Mumbai local train bombings, which killed more than 180 people, and in the 2010 German Bakery blast in Pune.
Do You Know:
• Markaz Taiba, Muridke—Hafiz Saeed’s headquarters, nerve centre of Lashkar-e-Taiba: The Markaz Taiba in Muridke in Pakistan’s Punjab province is the headquarters of the Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT), and its front, the Jamaat-ud-Dawa (JuD). Besides being a site of training and recruitment, the sprawling 200-acre campus serves as the ideological nerve centre of the LeT. It is here that all key terror attacks of the Lashkar are planned and directed, sources said.
—The facility lies 18-25 km away from the international border (IB), the Army said on Wednesday, adding that terrorists involved in the 2008 Mumbai attacks — including Ajmal Kasab and David Headley — were trained here.
• Sawai Nala camp, Muzaffarabad—This camp in Pakistan Occupied Kashmir (PoK) is located 30 km from the LoC, and is the LeT’s most important training centre. The Army said on Wednesday that the terrorists behind the attacks in Sonmarg and Gulmarg last October, and Pahalgam on April 22, were trained here. The name of this camp also came up after the 2000 Red Fort attack.
• Syedna Bilal camp, Muzaffarabad—Camp for Lashkar and Jaish, terrorist recruits are provided training by Pakistani special forces. The Indian Army said on Wednesday that this camp was the main staging area for the Jaish-e-Mohammed in PoK, and served as a centre for weapons, explosives, and jungle-survival training. It is located on the Neelum river opposite the Red Fort in Muzaffarabad.
• Barnala camp, Bhimber—Close to the LoC, training camp for mountain and jungle terrain, launchpad for infiltrators. Located 9 km from the LoC in PoK, this is a training centre for weapons handling, assembling IEDs, and jungle-survival, the Army said on Wednesday.
Security sources said the camp came up in the 1990s, and is used by both the LeT and the JeM terrorist groups. Sources said the camp specialised in preparing militants for mountainous and forested terrains which they would have to reckon with while infiltrating into J&K.
• Abbas camp, Kotli—Indoctrination centre and school for fidayeen recruits, located close to Pakistani military camp. The Army said on Wednesday that the camp, located 13 km from the LoC in PoK and only 2 km from the Kotli military camp, is used to prepare fidayeen fighters — suicide attackers — for the JeM. Sources in the security establishment said this camp too came up in the 1990s. It provides close-quarters battle (CQB) training, breaching and hostage-taking drills, and indoctrination focusing on martyrdom (shahadat) missions.
• Sarjal camp, Narowal—Near International Border in Pakistani Punjab, regrouping site before specialised terror training. This camp lies 6 km away from the IB in Pakistan’s Punjab province. The Army said the terrorists who killed four J&K police personnel in March 2025 in Kathua, Jammu, were trained here.
• Mehmona Joya camp, Sialkot—Initial induction centre for terrorists who infiltrate through Punjab and Jammu. Hizbul Mujahideen camp lies 12-18 km from the IB in Sialkot district in Pakistan’s Punjab province. This facility is used as a launchpad for Hizb terrorists to enter the Jammu region, as well as a training centre for operations and weapons handling.
• Gulpur camp, Kotli—Base of Lashkar units active in Rajouri and Poonch districts.
The Army said on Wednesday that this camp, located 30 km from the LoC in PoK, is a base of LeT units active in Rajouri and Poonch districts. Terrorists involved in the April 20, 2023 attack in Poonch, and the June 9, 2024 attack on a bus carrying pilgrims were trained here, the Army said.
• Markaz Subhanallah, Bahawalpur—Markaz Subhanallah in Bahawalpur in Pakistan’s Punjab province is the headquarters of the Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM). According to the Army, it is 100 km away from the IB, and serves as a centre for recruitment, training, and indoctrination.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍Operation Sindoor targets 9 locations: Links to LeT and JeM, how they’ve attacked India in the past
Precision guided long range weapons in Indian military’s arsenal
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
Mains Examination:
• General Studies III: Achievements of Indians in science & technology; indigenization of technology and developing new technology.
• General Studies III: Role of external state and non-state actors in creating challenges to internal security
What’s the ongoing story: India has not revealed what weapons were used in Operation Sindoor early on Wednesday morning (May 7). The official statement said that the Indian Armed Forces carried out precision strikes, hitting terrorist infrastructure deep inside Pakistan and in Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK).
Key Points to Ponder:
• Which precision-guided munitions were employed by the Indian Air Force during Operation Sindoor?
• Know about the SCALP missile.
• Which aircraft in the Indian Air Force has been modified to carry the air-launched variant of the BrahMos missile?
• The BrahMos missile is a joint venture between India and ?
• What best describes loitering munitions used in modern warfare?
• What is the significance of the “fire-and-forget” capability in missiles like BrahMos?
• How do weapons like HAMMER, SCALP, and BrahMos enhance India’s deterrence posture?
Key Takeaways:
• Twenty-one terror camps across nine locations were hit as part of the operation launched in retaliation for the attack by Pakistani terrorists on innocent civilians in Pahalgam last month.
• During Wednesday’s official briefing, Wing Commander Vyomika Singh, a helicopter pilot with the IAF, said niche-technology weapons with carefully selected warheads were used to avoid collateral damage.
• Over the past several years, the Indian military has built up a formidable arsenal of new-age weapons that includes a range of precision-guided long-range weapons and drones, including loitering munitions.
Do You Know:
• HAMMER: The Highly Agile and Manoeuvrable Munition Extended Range (HAMMER) air-to-ground precision-guided weapon system for the Rafale fighter aircraft has a range of up to 70 km, and can also be fitted to bombs and various guided systems.
—Built by the French aerospace, defence, and security corporation Safran, the HAMMER weapon system is highly versatile, and can be used for precision strikes against a range of targets in medium-range tactical operations.
—According to the Safran Group, the system is autonomous and insensitive to jamming, and can be launched from a low altitude over rough terrain.
• SCALP: This is an air-launched cruise missile with stealth features, designed for long-range deep strikes. SCALP-EG (Système de Croisière Autonome à Longue Portée — Emploi Général), known as Storm Shadow in Britain, can be operated at night and in all weather conditions.
—The missile, manufactured by the European multinational MBDA, has a range of 450 km, and is difficult to detect due to its low-flying capability when fired from an aircraft.
—Its advanced and highly accurate navigation system, which uses Inertial Navigation System (INS), Global Positioning System (GPS) and terrain referencing, can penetrate bunkers and ammunition stores.
• METEOR: The Meteor is a new-generation Beyond Visual Range Air-to-Air Missile (BVRAAM) system which is effective in dense electronic-warfare environments.
According to its manufacturer MBDA, the missile’s solid-fuel ‘ramjet’ motor provides it with thrust all the way to the target intercept, and thus the largest ‘No Escape Zone’ of any air-to-air missile system.
• BRAHMOS: These supersonic cruise missiles, which have been operationalised in all three defence services, are built by BrahMos Aerospace, a joint venture between India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and Russia’s NPO Mashinostroyeniya.
—BrahMos missiles operate at close to Mach 3 speed in the cruise phase, which ensures reduced flight time, lower dispersion of targets, and quicker engagement time and non-interception
• LOITERING MUNITIONS: They are used for surveillance and identification of targets, and can carry out precision strikes, autonomously or otherwise. The Armed Forces in the last few years have been procuring a range of drones, including loitering munitions.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍Operation Sindoor and beyond: Think about the Pakistan challenge, long-term
ECONOMY
US Fed holds interest rates steady, cites inflation risks
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Current events of national and international importance.
Main Examination: General Studies II: Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests.
What’s the ongoing story: The Federal Reserve on Wednesday, May 7,held its key interest rate unchanged as it waits for the Trump administration’s trade policy to take shape and sees its impact on the economy.
Key Points to Ponder:
• Who is Jerome Powell?
• What is the U.S. Federal Reserve?
• What does the Fed do?
• What does unchanged rates mean?
• Why Did the Fed Hold Rates?
• The U.S. Federal Reserve and Reserve Bank of India—Compare and Contrast
• Indian government vs RBI—any instances of friction?
• Politics of governments and tenures of RBI Governors—Know in detail
• What do you understand by the term ‘Federal Tapering’?
Key Takeaways:
• The decision, widely expected amid rising economic and political uncertainty sweeping the political and economic landscape, the Federal Open Market Committee held its benchmark overnight borrowing rate in a range between 4.25%-4.5%, where it has been since December. “Uncertainty about the economic outlook has increased further,” the Fed said in a post-meeting statement, noting growing risks of both higher inflation and rising unemployment.
• Interest rates on credit cards, personal loans, and auto loans are unlikely to rise, but they won’t fall either. Adjustable-rate mortgages may also hold steady, while fixed mortgage rates depend more on long-term bond yields. Banks typically follow the Fed’s lead.
• The Fed’s decision stems from a mix of inflation concerns and uncertainty driven by trade policy. Chair Jerome Powell said the current stance of monetary policy gives the Fed flexibility to respond quickly to changing economic conditions. A Federal Reserve survey highlighted a sharp decline in business sentiment due to uncertainty over Donald Trump’s trade moves — particularly his tariff threats. Powell noted that the tariff impact has been “significantly larger than anticipated,” and if sustained, could fuel inflation, slow growth, and ultimately increase unemployment.
Do You Know:
• The US central bank system performs five broad functions to promote the effective operation of the American economy. The Federal Reserve identifies these functions as follows:
—conducting the US monetary policy to promote maximum employment and stable prices;
—promoting the stability of the financial system and seeking to minimize and contain systemic risks through active monitoring and engagement in America and overseas;
—promoting the safety and soundness of individual financial institutions and monitoring their impact on the financial system as a whole;
—fostering safety and efficiency in the payment and settlement system through services to banks and the federal government that facilitate US-dollar transactions and payments;
—promoting consumer protection and community development through consumer-focused supervision and examination, research and analysis of emerging consumer issues and trends, and the administration of consumer laws and regulations.
• The Federal Reserve System consists of three major entities:
—The Federal Reserve Board of Governors (Board of Governors), the main governing body of the system. The chairman and governors of the Board are appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate. The offices of the Board of Governors are headquartered in the Marriner S Eccles Federal Reserve Board Building in Washington DC.
—The Federal Reserve Banks (Reserve Banks), are the regional operating arms of the Federal Reserve System, and are supervised by the Board of Governors. There are 12 Federal Reserve Banks (such as those of New York, Boston, Philadelphia, Atlanta, Chicago, San Francisco, etc.) corresponding to the 12 Federal Reserve Districts in the US.
—The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) consists of the members of the Board of Governors and presidents of the Reserve Banks. The chair of the Board is the chair of the FOMC. The FOMC has 12 members at a time: seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining 11 Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
Other Important Articles Covering the same topic:
📍Explained: Federal Reserve signals, and Indian markets
Previous year UPSC Prelims Question Covering similar theme:
4. Indian Government Bond Yields are influenced by which of the following? (2021)
1. Actions of the United States Federal Reserve
2. Actions of the Reserve Bank of India
3. Inflation and short-term interest rates
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
| PRELIMS ANSWER KEY |
| 1.(c) 2.(b) 3.(c) 4.(d) |
For any queries and feedback, contact priya.shukla@indianexpress.com
Subscribe to our UPSC newsletter. Stay updated with the latest UPSC articles by joining our Telegram channel – IndianExpress UPSC Hub, and follow us on Instagram and X.
Must Read
Buzzing Now



Jun 06: Latest News
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
























